Embracing Disruption
Created in China: Humanoid Robots

Over recent years, much of the media attention on China has been related to macro challenges – geopolitical conflicts, the weakness of the property sector and deflationary pressures. In our view, this focus has distracted investors from the rapid pace of development in China’s technology space.
Indeed, US trade restrictions designed to prevent Chinese companies from sourcing high spec technology components, aimed at stifling Chinese innovation, have instead served to reinforce China’s push to become increasingly self-reliant in critical industries of the future. It is in this context that the launch in January of DeepSeek – China’s answer to ChatGPT – shocked the technology world.
But while the DeepSeek announcement has been widely publicised because of its impact on technology stocks around the world, there have been a number of additional signs pointing to China’s ‘under the radar’ progress. This piece, covering humanoid robots, is the first in a new series that will highlight China’s new areas of technological innovation. Over time, we believe that these will provide significant investment opportunities.
Humanoid robots – the next revolutionary technology?
Humanoid robots, unlike industrial robots, are designed to mimic humans in both form and function – machines capable of thinking and behaving like a real person. While commonly depicted in movies set in the distant future, significant investment and sooner-than-expected progress in artificial intelligence and hardware engineering have brought us closer to seeing humanoid robots integrated into everyday lives.
With a wide scope of application, humanoid robots have the potential to transform industries, boost productivity, and fundamentally redefine the way we interact with technology.
Humanoid robot development was popularized in 2021 when leading electric vehicle brand Tesla announced development plans for its general-purpose humanoid robot “Optimus”. Just four years later in January 2025, fourteen humanoid robot models from emerging industry leaders proudly stood on the stage at the Consumer Electronics Show (CES) in Las Vegas, the premier global technology trade exhibition. On the same stage, Jensen Huang, CEO of Nvidia, declared that “the ChatGPT moment for general robotics is just around the corner”, predicting Nvidia’s products to power a billion humanoid robots in the coming
The total addressable market for humanoid robots is projected to reach USD 38 billion by 20352. There is a wide range of potential applications across various fields.
With time, humanoid robots could for example, evolve to perform surgeries with precision. As a first step in this direction, a Korean company has just received FDA approval in the US to use its robots in brain surgery3. In education they could serve as teaching assistants and provide support in classrooms. And in manufacturing, humanoid robots could work alongside people handling tasks that are repetitive, dangerous or require high precision. This is another field where we see further signs of progress – Amazon, the US online retailer has started testing the use of humanoid robots to move boxes and sort packages alongside human employees in distribution warehouses4.
And over time, functionalities that address the needs of the mass consumer market, such as a live-in housekeeper or a companion for the elderly, are expected to be to drivers for broader adoption.
China’s key role in the sector’s evolution
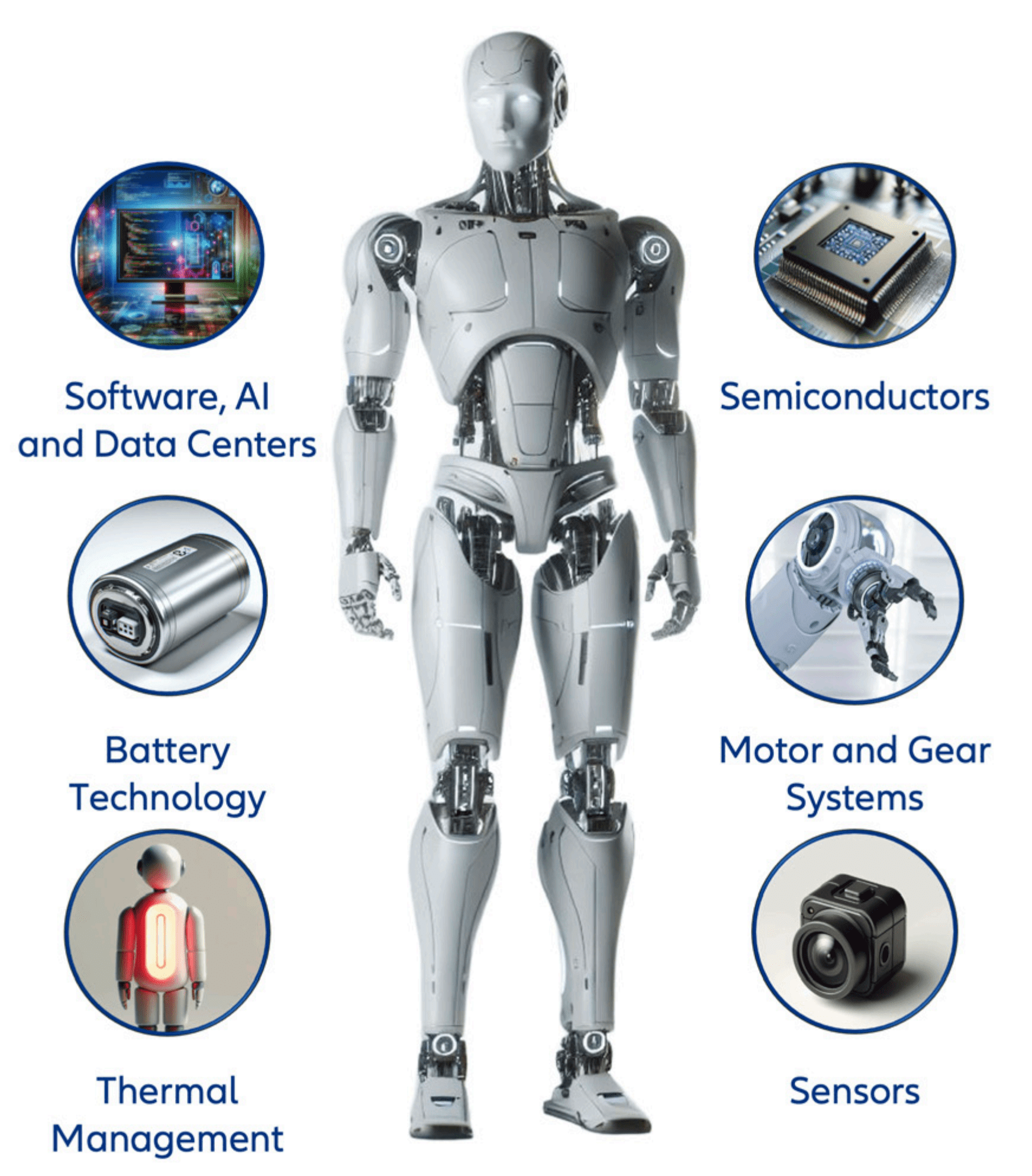
While much of the global spotlight related to humanoid robots so far has been on US-led developments, Chinese companies already play a critical role in the sector’s evolution as a provider of key components underlying robotic functions. This includes high precision sensors, control systems, motor parts, efficient battery solutions, and semiconductor technology.
With China’s deep industrial value chains and manufacturing advantages, the gap in product quality between Chinese-produced components and those made by US and Japan competitors has been narrowing. And as industry leaders race to bring humanoid robots to the mass-market, Chinese companies continue to provide the scale and cost advantages needed to bring humanoid robots to commercialization.
Holding around two-thirds of global robotics patents5, China has been the world’s largest market for industrial robots for over a decade6 and has made significant advancements in automation and autonomous technologies. This expertise in industrial robotics is the foundation for its clout in the emerging field of humanoid robotics. In fact, four out of the fourteen humanoid models that stood on stage with Jensen Huang a the 2025 CES event were developed by Chinese companies.
Beyond industrial settings and trade shows, robots have also started to become a more familiar presence in everyday lives in China. They can be found checking guests into hotels, delivering food to customer tables at hotpot restaurants, and even climbing the Great Wall of China alongside tourists.
Humanoid robots even made a recent appearance in the nation-wide Chinese Lunar New Year television broadcast, an annual spectacle drawing more than a billion viewers in China. During the four-hour program, humanoid robots took to the stage performing an intricately choreographed folk dance among professional dancers. A behind-thescenes video showed the robots carefully rehearsing dance steps, shaking hands, and posing for selfies7.
New technologies inevitably take time to become widely accepted and understood. However, China’s growing integration of smart applications into everyday life serves as an example of ways to bridge the gap between hardware engineering and humanfocused design that is at the center of humanoid robot applications.
Source: AllianzGI, January 2025
Conclusion
In our view, China’s long-term economic objective is to build a future growth model based on technology-intensive manufacturing, and in so doing to reduce the previous reliance on property and infrastructure. Over time we expect that this will result in a more dynamic and diverse investment universe. Humanoid robots are just one area of innovation that investors may want to consider when investing in China’s future technologies.
Capturing investment opportunities related to humanoid robots
Already there are a number of listed companies that have invested significant capital and human resources to the development of humanoid robots. Examples include:
- Zhejiang Shuanghuan Driveline – a producer of transmission systems used in automobiles and power electric systems that transform battery power into mechanical movement in robotic limbs. The company holds a portfolio of over 400 patents in power management, electric motor, and control algorithms design8.
- Zhejiang Sanhua Intelligent Controls – a Chinese developer of motion and thermal control systems to enable smooth, precise movement in robots. The company currently supplies thermal management technology for Tesla’s electric vehicles and is expected to further this partnership and supply key components for Optimus, Tesla’s humanoid robot.
- Cambricon Technologies – an AI chip designer in China with a focus on high-performance solutions for computer vision and language processing needed to efficiently develop and deploy AI models tailored for humanoid robots.
1 Ctech, as of 27 January 2025
2 Goldman Sachs, as of 8 January 2024
3 Korea Economic Daily, as of 21 January 2025
4 Bloomberg, as of 4 March 2024
5 International Federation of Robotics, as of 30 September 2023
6 China Briefing, as of 30 January 2025
7 SCMP, as of 4 February 2025
8 Zhejiang Shuanghuan Driveline company website, as of 10 February 2025






